The progression of hair thinning and hair loss varies depending on gender and age, and various factors are involved.
It is known that 40% of men experience significant hair loss (alopecia) by the age of 35. By age 60, this number reaches 65%.
Additionally, 50-75% of women will experience significant hair loss by the age of 65. As we age, it is common for hair density to decrease and hair to become thinner overall.
Hair Cycle
Throughout your life, your hair goes through a cycle of growth and shedding. This “hair cycle” has three stages: growth, regression, and resting. The most common cause of hair thinning is disruption of this cycle. Specifically, hair falls out more easily as the growth phase becomes shorter and the resting phase becomes longer.
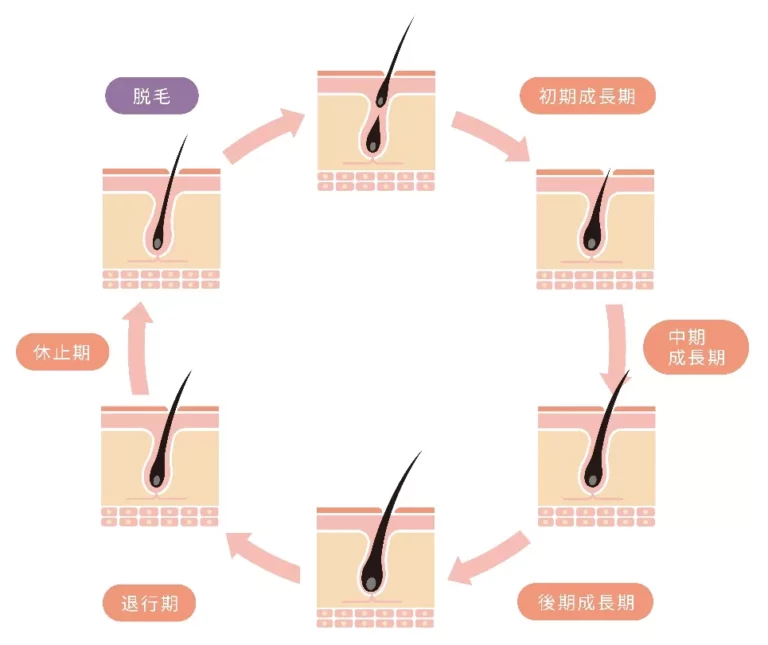
1. Growth Period (Anagen Period)
– This is the period when hair growth is most active.
– It usually lasts 2 to 7 years, but this period tends to be shorter for people with thinning hair. In other words, the hair does not grow enough and falls out.
2. Catagen Phase
– This is a short period when hair growth stops, the hair root shrinks, and the hair goes into rest. Approximately 1-2% of all hair is at this stage.
– The period is approximately 2 to 3 weeks.
3. Telogen Phase
– The period during which your hair is preparing to fall out. It is natural for hair to fall out at this point, but for people with thinning hair, this period often lasts longer. If you lose a lot of hair before new hair grows, thinning hair will be more noticeable.
– The period is approximately 3 to 4 months.
Hair Loss
The number of hairs that fall out per day is usually between 50 and 100. This is a natural process and part of the hair cycle. If it falls out any further, care will be required.

Causes of Thinning Hair
There is not just one cause for thinning hair, but a variety of factors are intertwined. Here are six causes that are particularly interesting and worth knowing about.

1. Genetics
Genetics is one of the major causes of hair loss. Male pattern baldness (AGA) is especially likely to occur if you have a family history of thinning hair. This is caused by genetic factors that cause your hair to become thinner and have a shorter growth period.

2. Hormonal Influence
When your hormones are out of balance, your hair will also be affected. In particular, DHT (dihydrotestosterone), a type of male hormone, has a negative effect on the hair roots and causes hair thinning. For women, hormonal imbalances can also affect hair, especially during menopause and postpartum hair loss.

3. Stress
Stress is the enemy of hair. In today’s busy society, it is rare for the mind and body to rest, which affects hair growth. Continuing stress can disrupt the hair cycle and cause hair to enter the resting phase.
4. Malnutrition
Nutrition is essential for hair health. In particular, deficiencies in iron, vitamins, and zinc can slow hair growth and increase hair loss. Eating a balanced diet will have a positive effect on your hair. If you cannot compensate with food alone, consider using supplements.

5. Deterioration of the Scalp Environment
The scalp is the “foundation” on which hair grows. Therefore, if the scalp environment is poor, hair growth will also be adversely affected. When excess sebum, dandruff, and inflammation occur on the scalp, the hair roots become weak and hair falls out easily. It is important to maintain a healthy scalp environment with proper shampoo and scalp care.

6. Aging
As you get older, your hair cycle gets shorter, and your hair becomes thinner. However, rather than giving up because of your age, it is possible to maintain healthy hair depending on your lifestyle and care. For example, scalp massage and moderate exercise promote blood circulation, which has a positive effect on hair.
